Patients with EPI are also managing underlying disorders1-4

Percentage of patients with EPI by underlying condition

Surgery for pancreatic neoplasms. The Whipple procedure is associated with the highest rate of EPI (85%–95%), while pylorus-preserving intervention has a slightly lower rate (80%–90%).1

*Surgery for pancreatic neoplasms. The Whipple procedure is associated with the highest rate of EPI (85%–95%), while pylorus-preserving intervention has a slightly lower rate (80%–90%).1
In a survey of 500 clinicians and
1,001 adult patients with chronic GI issues5:
≈4 years
was the average amount of time until
patients with chronic GI symptoms
sought medical help5
1 in 4
patients with EPI were originally
diagnosed with another
GI condition5
EPI is primarily a clinical diagnosis, but it can be easy to overlook6
GI symptoms could indicate EPI, another disorder, or both7-19

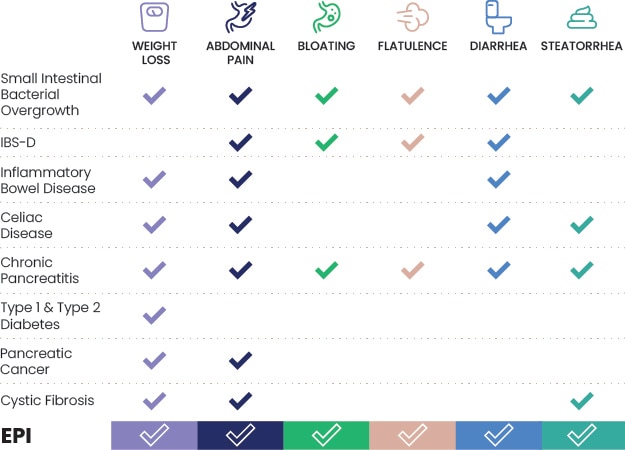
Steatorrhea occurs in patients with severe EPI20
This chart is for informational purposes only. It is not a complete list of symptoms for each disorder and is not intended to be used to diagnose, treat, or care for any particular patient.
If a patient presents with these symptoms, especially if they get worse after a fatty meal, it could be EPI21
PERT is frequently underdosed—an effective starting dose could require more lipase than you realize6,20
480,000 to 960,000 lipase units may seem high, but that's what a healthy pancreas produces each meal22†
For patients with EPI and CP, the ACG-recommended adequate dosage of PERT is AT LEAST 40,000 to 50,000 lipase units per meal23
The estimated “normal” amount of pancreatic enzyme secretion 4 hours after a meal varies with content and volume of meal ingested. Data estimated from a study using test meals of 300 to 600 k/cal.
Effective management of EPI depends on6,19,24:
Adequate dosing of a PERT
such as ZENPEP®
Lifestyle and
dietary modifications
Maintaining adequate nutritional status with vitamin/nutrient supplements
The ACG identifies improved nutrient absorption and GI symptom relief as important treatment goals in patients with EPI and CP.23
CP=chronic pancreatitis; EPI=exocrine pancreatic insufficiency; GI=gastrointestinal; IBS-D=diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome; PERT=pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy.
References: 1. Capurso G, Traini M, Piciucchi M, Signoretti M, Arcidiacono PG. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency: prevalence, diagnosis, and management. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2019;12:129-139. doi:10.2147/CEG.S168266 Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2019;12:129-139. doi:10.2147/CEG.S168266 2. Leeds JS, Hopper AD, Sidhu R, et al. Some patients with irritable bowel syndrome may have exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;8(5):433-438. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2009.09.032 3. Maconi G, Dominici R, Molteni M, et al. Prevalence of pancreatic insufficiency in inflammatory bowel diseases. Assessment by fecal-elastase-1. Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53(1):262-270. doi:10.1007/s10620-007-9852-y 4. Celiac disease and exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. Beyond Celiac. Accessed November 7, 2023. https://www.beyondceliac.org/celiac-disease/related-conditions/pancreatic-insufficiency/ 5. Kirsch B. Widespread lack of awareness of pancreatic insufficiency. MDedge News. Published December 16, 2016. Accessed November 6, 2022. www.mdedge.com/gihepnews/article/120327/ibd-intestinal-disorders/widespread-lack-awareness-pancreatic-insufficiency 6. Perbtani Y, Forsmark CE. Update on the diagnosis and management of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. F1000Res. 2019;8:F1000 Faculty Rev-1991. doi:10.12688/f1000research.20779.1 7. Malik Z. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO). Merck Manual. Updated March 2023. Accessed October 2, 2023. https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/digestive-disorders/malabsorption/small-intestinal-bacterial-overgrowth-sibo 8. Mayo Clinic Staff. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO). Mayo Clinic. Published January 6, 2022. Accessed October 2, 2023. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/small-intestinal-bacterial-overgrowth/symptoms-causes/syc-20370168 9. Wald A. Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome in adults. UpToDate. Updated July 20, 2022. Accessed October 2, 2023. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/clinical-manifestations-and-diagnosis-of-irritable-bowel-syndrome-in-adults 10. What is Crohn’s disease? Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation. Accessed October 2, 2023. https://www.crohnscolitisfoundation.org/what-is-crohns-disease 11. What is ulcerative colitis? Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation. Accessed October 2, 2023. https://www.crohnscolitisfoundation.org/what-is-ulcerative-colitis 12. Symptoms of celiac disease. Celiac Disease Foundation. Accessed October 2, 2023. https://celiac.org/about-celiac-disease/symptoms-of-celiac-disease/ 13. Mayo Clinic Staff. Pancreatitis. Mayo Clinic. Published September 23, 2023. Accessed October 2, 2023. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pancreatitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20360227 14. Felman A, Villines Z. What to know about chronic pancreatitis. Updated January 4, 2023. Accessed October 2, 2023. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/160459 15. Mayo Clinic Staff. Type 1 diabetes. Mayo Clinic. Published September 15, 2023. Accessed October 2, 2023. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/type-1-diabetes/symptoms-causes/syc-20353011 16. Mayo Clinic Staff. Type 2 diabetes. Mayo Clinic. Published March 14, 2023. Accessed October 2, 2023. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/type-2-diabetes/symptoms-causes/syc-20351193 17. Mayo Clinic Staff. Pancreatic cancer. Mayo Clinic. Published September 8, 2023. Accessed October 2, 2023. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pancreatic-cancer/symptoms-causes/syc-20355421 18. Mayo Clinic Staff. Cystic fibrosis. Mayo Clinic. Published November 23, 2021. Accessed November 7, 2023. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cystic-fibrosis/symptoms-causes/syc-20353700 19. Alkaade S, Vareedayah AA. A primer on exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, fat malabsorption, and fatty acid abnormalities. Am J Manag Care. 2017;23(suppl 12):S203-S209. 20. Brennan GT, Saif MW. Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy: a concise review. JOP. 2019;20(5):121-125. 21. Whitcomb DC, Duggan SN, Martindale R, et al. AGA-PancreasFest joint symposium on exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. Gastro Hep Advances. 2023;2(3):395-411. 22. Keller J, Layer P. Human pancreatic exocrine response to nutrients in health and disease. Gut. 2005;54(suppl 6):vi1-vi28. doi:10.1136/gut.2005.065946 23. Gardner TB, Adler DG, Forsmark CE, Sauer BG, Taylor JR, Whitcomb DC. ACG Clinical Guideline: chronic pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115(3):322-339. doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000000535 24. Ockenga J. Importance of nutritional management in diseases with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. HPB (Oxford). 2009;11(suppl 3):11-15. doi:10.1111/j.1477-2574.2009.00134.x
