Up to 90% of patients diagnosed with CF have EPI.1
Early diagnosis and proper treatment can improve nutrient absorption and symptoms2
Left untreated, EPI can compromise a growing child in many ways3
- Malabsorption leading to vitamin and nutrient deficiencies
- Impaired height and weight
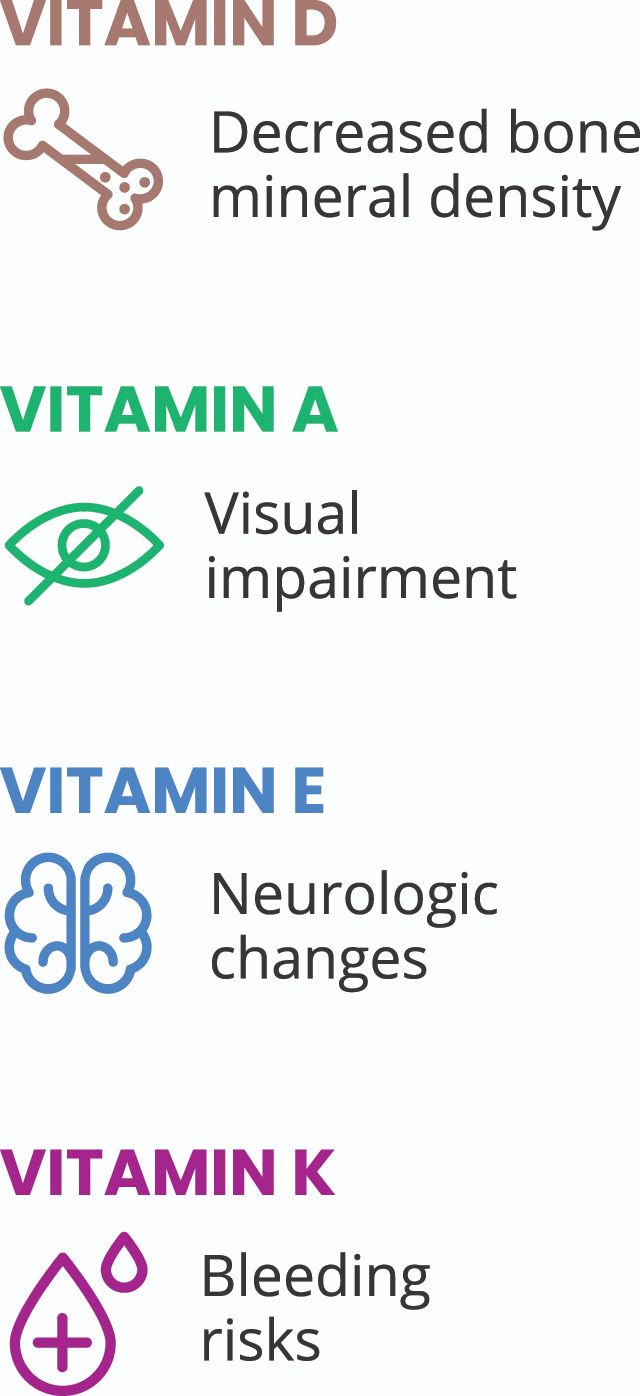

According to the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Guidelines3:
- The dangers of nutritional deficiency and negative consequences of eating associated with abdominal symptoms argue strongly in favor of proactive treatment
Symptoms of EPI develop when ≈90% of exocrine function is lost2-5
EPI may cause the following symptoms2,6,7:
- Abdominal pain
- Bloating
- Excessive flatulence
- Frequent stools
- Nausea
- Malaise
- Diarrhea
- Steatorrhea
Poor nutritional status associated with untreated EPI may lead to poorer outcomes in patients with CF8
Effective management of EPI depends on6:
Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy, such as ZENPEP®
Dietary modifications
Regular nutritional assessment as a component of routine care
The Cystic Fibrosis Foundation states that patients with laboratory evidence of EPI should be started on PERT even in the absence of signs of fat malabsorption.7
CF=cystic fibrosis; EPI=exocrine pancreatic insufficiency; PERT=pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy.
References: 1. Capurso G, Traini M, Piciucchi M, Signoretti M, Arcidiacono PG. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency: prevalence, diagnosis, and management. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2019;12:129-139. doi:10.2147/CEG.S168266 2. Perbtani Y, Forsmark CE. Update on the diagnosis and management of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. F1000Res. 2019;8:F1000 Faculty Rev-1991. doi:10.12688/f1000research.20779.1 3. Othman MO, Harb D, Barkin JA. Introduction and practical approach to exocrine pancreatic insufficiency for the practicing clinician. Int J Clin Pract. 2018;72(2):e13066. doi:10.1111/ijcp.13066 4. Ockenga J. Importance of nutritional management in diseases with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. HPB (Oxford). 2009;11(suppl 3):11-15. doi:10.1111/j.1477-2574.2009.00134.x 5. Johnson CD, Arbuckle R, Bonner N, et al. Qualitative assessment of the symptoms and impact of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency (PEI) to inform the development of a patient-reported outcome (PRO) instrument. Patient. 2017;10(5):615-628. doi:10.1007/s40271-017-0233-0 6. Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. Pancreatic Enzymes Clinical Care Guidelines. Accessed September 29, 2023. https://www.cff.org/pancreatic-enzymes-clinical-care-guidelines#pancreatic-enzymes-clinical-care-guidelines-executive-summary 7. Borowitz D, Robinson KA, Rosenfeld M, et al. Cystic Fibrosis Foundation evidence-based guidelines for management of infants with cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr. 2009;155(suppl 6):S73-S93. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.09.001
